‘Natural’ solutions for dry slopes with TeMa products
Environment, climate, energy, territorial planning, natural risk prevention, and water resource research and management are what researchers and planners have to deal with today in connection with environmental works. These are all ‘watchwords’ in the modern world of geotechnics, which require specific know-how and the use of suitable materials, in the awareness that the search for solutions is constantly evolving. With a proactive approach that provides geotechnical applications for soil protection, and expertise to aid the sustainable management of processes, we can now carry out the required works while making the land safe and harmonising the landscape.
Surface water shapes the soil, now more than ever before, due to the increase in extreme events. Today, there is a growing awareness that the ‘natural’ resources we have at our disposal are capable of limiting the effects of scouring and runoff. On dry slopes, for example, soil erosion is the process whereby materials are removed by the mechanical and chemical actions of wind and water. From a technical/scientific perspective, a further distinction is made: in addition to the concept of soil erosion , there is soil loss and sediment yield .
The effect of weathering on the soil is therefore a phenomenon to be foreseen and controlled. On the surface, the causes cannot always be detected, but a Geologist – after carrying out the necessary research – will pinpoint the problems and recommend solutions.
The main phenomena associated with soil depletion are:
- the thickness of arable soil, which includes organic substances, water, mineral salts and fine particles, decreases on a local scale: within a few generations, fertile soil can become arid;
- accelerated and uncontrolled surface erosion can cause landslides on steep slopes, increasing the extent and intensity of crumbling to the point of destroying the vegetation cover of an entire slope;
- eroded material is carried downhill, thereby reducing the capacity of watercourses and thus increasing the risk of flooding;
- the sedimentation of eroded material that ends up in irrigation channels decreases their efficiency and service life;
- eroded material, often laden with chemicals from agricultural practices such as fertilisers and insecticides, instead of being absorbed by the soil, becomes concentrated in watercourses, spreading pollution over a wider area.
The new design concept – determined by precise environmental choices – undoubtedly promotes sustainability. In this respect, on dry slopes, soil ‘helped’ by suitable products to encourage revegetation becomes a very strong ‘barrier’ to inclement weather over time.
By observing the grassed embankments bordering major road and railway routes, we can appreciate the need, which is met, to protect the safety of infrastructures against problems of topsoil slippage. These are artificial embankments, created to meet technical requirements. They were therefore barren at the time of construction, and hence exposed to the impact and removal of soil by rainwater. Ensuring grassing therefore increases the level of safety, improves visual impact and, last but not least, respects biological diversity that is preserved.
New TeMa Geo Solutions materials make these solutions possible. To encourage vegetation to take root, TeMa has come up with K-Mat synthetic geomats and biomats in natural fibre matting (straw, coconut and jute), ECOVERMAT and ECOVERNET, in addition to the X-Grid PET-C AMrange of geomats, which are also useful for reinforcing slopes.
TeMa, an Italian company established in 1993, has gained experience on 4 continents with products for the world of geotechnics, which are trusted by planners and contractors. Over 30 years of providing geotechnical solutions that aid the soil with its own erosion control and stabilisation potential, resulting in a clear environmental advantage.
- Published in Dry slopes, Erosion mats, GEO
System for reinforced soil retaining structures
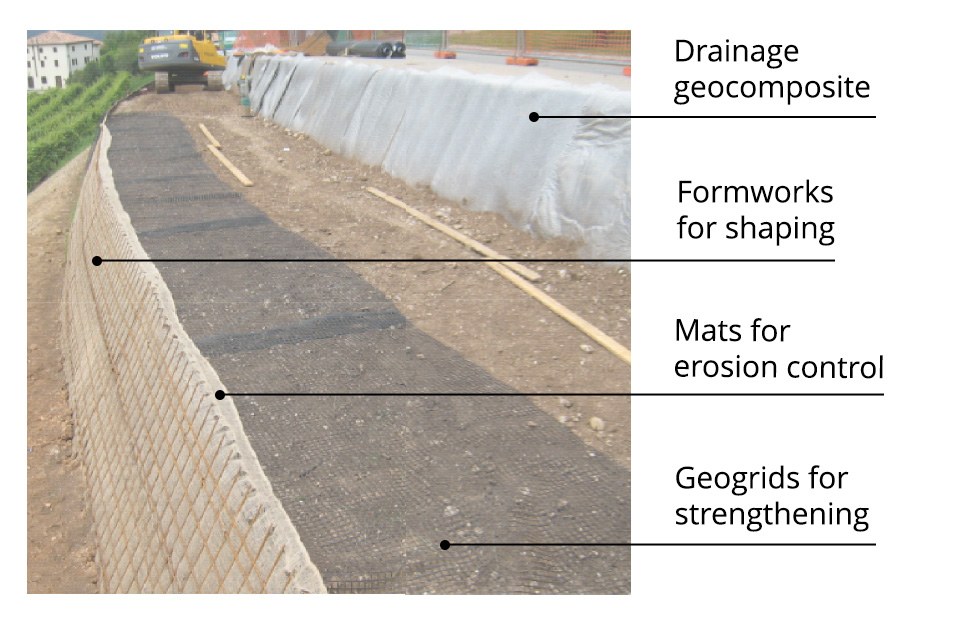
T-System is the system from TeMa Geo Solutions that includes various components for strengthening, surface erosion control, drainage and retaining used in the construction of reinforced soil retaining structures: innovation that we’ve been exploring here at TeMa since our inception 30 years ago, and that is now one of our hallmarks. Let’s take a more detailed look below.
Components for strengthening
Designed for strengthening, the knitted X-Grid PET C geogrids are made from high-strength polyester yarn, with a protective polymer coating. They deliver tensile strength in the 20 kN/m to 800 kN/m range.
Components for erosion control
They protect the face of the structure from erosive agents, like wind and driving rain, until the vegetation has had time to establish. TeMa Geo Solutions offers natural solutions made from cellulose fibres, like Ecovermat, or jute fibres, like Ecovernet, as well as synthetic solutions made from monofilaments (K-Mat F), polypropylene (K-Mat FA) or fibreglass (K-Mat FG Green).
Components for drainage
Drainage geocomposites like Q-Drain are used to address the problem of water seeping into the backfill.
Components for retaining
We have a line of facings made from electrically welded wire mesh — with inclinations ranging from 65° to 80° — to ensure the exposed face is straight.
Practical tips
On site
System components must be stored well away from machinery, and suitably protected from dust or residues from work on site.
To avoid excessive overlaps and waste, the X-Grid geogrids must be cut to size using a suitable metal stand with metal trestles supporting a circular rod to be inserted inside the roll.
Erosion control components — whether biodegradable or synthetic — must be stored in a dry place and not in direct contact with the natural ground, so as to avoid laying problems later on.
Metal formwork must be stored well away from areas where machinery is operating, and carried in only when it is time to install.
During assembly, it is best to apply U-shaped strips of rubber or metal so that the geogrids can be wrapped correctly over the formwork without getting caught on the top of the bars. (see photo)
Special instructions
We advise against backfilling with silty and clayey material; at the very least, only use this kind of material after mixing it with aggregate.
The full range of system components comes with instructions on the relevant procedures to be followed. Contact us, we’ll be happy to provide case studies and full information.
Safety first: and that applies to landfills, too
TeMa Geo Solutions’ thirty years of experience extends to the field of controlled landfills and contaminated sites, with products specially designed for each function to ensure the site is safe, and with investment-conscious solutions, as well as a focus on ensuring peak performance.
Safe landfills legislation
In Italy, regulation around the controlled disposal of waste dates back as far as 1982, later supplemented by the European directive and updated in 2020 by Italian legislation (D.Lgs no.121).
This legislation covers all aspects of the disposal cycle, from landfill classification to the type of waste, as well as criteria for the construction and operation of the facilities, with a strong environmental focus. In this regard, TeMa has come up with built-up systems and materials that fulfil the required functions and comply with the relevant legislation.
The main functions to make safe a controlled landfill
Making safe a landfill facility entails fulfilling a number of functions:
![]() Barrier
Barrier
Walls and floor must be isolated to protect groundwater and soil from leachate and biogases resulting from decomposition processes. To ensure sufficient watertightness, legislation requires the use of at least 0.5 m of clay or, drawing on the principle of hydraulic equivalence, synthetic products: sodium bentonite composites like Barrier Bento — which contains up to 5 kg of bentonite/sqm sandwiched between two geotextiles — provide an impermeable layer, acting as a barrier between soil and waste.
![]() Reinforcement
Reinforcement
One of the major issues to be addressed when designing landfills, especially the capping system, is stability, which can be achieved by leveraging the compressive strength of the soil combined with the tensile strength of geosynthetics. Reinforcement solutions provided by TeMa range from PET-series geogrids to geomats laminated with geogrids.
![]() Drainage
Drainage
For liquid and gas capture, legislation calls for the use of 50 cm of aggregate, which nonetheless can come with its own stability issues, especially on steeper slopes. With the use of drainage geocomposites, the relevant built-up system can be pared back, while the number of vehicles required to carry materials can also be reduced. TeMa’s offering ranges from studded and micro-studded membranes to monofilaments laminated with nonwovens, and geonets with one or two nonwoven layers.
![]() Erosion control
Erosion control
The top layer of the soil is eroded by the action of the elements — especially by the type of unpredictable and extremely violent weather events we’ve witnessed in recent years — triggering alarming landslips, which can undermine a site’s hydrogeology. To prevent issues of this kind, it’s essential to encourage vegetation (which serves as a form of natural erosion control) and protect the soil while it takes root by using natural or synthetic mats from TeMa.
TeMa at the 12th International Conference on Geosynthetics.
We too will be at the 12th edition of the International Conference on Geosynthetics that will take place in Rome, at the Parco della Musica auditorium from 17 to 21 September 2023, and which will involve a full programme of meetings between professionals (further information about the events here).
Four days of training and information meetings on geosynthetics, exploring all sub-types: woven and non-woven geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geomats, drainage and reinforcement geocomposites, and geomembranes.
Geosynthetics are becoming increasingly popular in applications and fulfil various functions (often combined). For example:
- Drainage – drainage geocomposites and geonets.
- Filtration and Separation – woven geotextiles and non-woven geotextiles.
- Reinforcement – woven geotextiles and geogrids.
- Protection of waterproofing – studded membranes with truncated conical or star-shaped studs.
- Erosion control – geonets, geomats, biotextiles.
- Mechanical protection – non-woven geotextiles, composite geotextiles.
- Special applications – various geosynthetics made to specific requirements.
The main topics discussed will cover various fields of application, including anti-seismic design to road and railway embankments, erosion control, filtration and drainage functions, as well as an analysis of case studies.
The world of research is continuously evolving and the scheduled meetings will provide an excellent opportunity for sharing experiences and recent technical developments with engineers, geologists, consultants, contractors and whoever is involved in research and using geosynthetics.
During the exhibition event visitors will be able to take part in technical conferences, the Giroud lecture, special lectures and short courses , as well as visit the exhibition hall to meet manufacturers.
TeMa has thirty years of experience in using geosynthetics
The international event, entitled ‘Leading the way to a resilient planet’, fully represents the reason why TeMa began to manufacture and experiment with geosynthetics from the mid-1990s onwards: to research the most suitable technologies and materials for use in the construction of buildings and geotechnical works.
We have been involved in continuous interaction, also due to an increased awareness of major environmental issues. This has enabled us to broaden our range of products and expand in 80 countries worldwide.
Today, our catalogue includes many products that meet specific requirements for landfills, tunnels, road embankments, river banks and reinforced earth structures, gradually increasing performance for surface erosion control, rainwater drainage, and the reinforcement of grassy slopes.
The geosynthetics sector is rapidly developing and we are making huge investments, especially in research, so as to supply our customers with the best solutions, also tailor-made, for their projects. We share the same ‘urgency’ as our partners to pursue our unwavering ideal of respecting the environment and the hydrogeological protection of the land.
We look forward to seeing you in Rome from 17 to 21 September 2023, at Stand 22.
Meanwhile, you can discover all the details about the event here.
Green surfaces and green roofs: benefits and technical ins and outs
In recent years, “green” has become more and more of a buzzword, encompassing simple and cost-effective solutions that can be adopted by anyone with a roof. We’re talking green roofs, which, in addition to bringing undeniable environmental benefits, are the perfect place for relaxing with the family or enjoying summer drinks with friends. The origins of roof gardens date back to ancient times — think Hanging Gardens of Babylon — and, today, are built for extreme reliability, including long service life, with excellent products producing even more advantages.
Let’s take a look at the full picture in detail.
The advantages of green areas
For the environment
Plants and grass are natural carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and releasing oxygen, in addition to filtering particulate matter. In addition, they lessen the urban microclimate effect by lowering temperatures by several degrees centigrade, and reduce electrosmog caused by any electronic device.
They muffle noise and, if designed well, absorb and retain the early sudden downpours associated with significant rain events.
A series of sustainable improvements for urban wellbeing, improving air quality with less smog and particulate matter.
For occupant comfort
Vegetation also acts as natural thermal insulation — which is no small advantage given the energy crises of recent months — and soundproofing in loft bedrooms. Furthermore, it provides the roof with effective protection against UV rays, mechanical stress and daily variations in temperature, thus increasing the average service life of waterproofing.
Lastly, creating a garden on a roof increases the value of the property.
From a technical point of view
A green roof build-up comprises a number of layers, including geosynthetics offering better performance than traditional systems in terms of drainage, mechanical protection of waterproofing, and filtration. The products used are lighter and non-bulky, easy to transport and quick to install.
Functions required of the roof
There are 4 main functions involved:
- Reservoir (to hold rainwater for irrigation purposes until it is needed) and drainage (to remove excess water). This combined function is addressed with 20mm HDPE studded membranes T-Kone H XL and T-Kone H XL S.
- Control of surface erosion caused by atmospheric agents. This function is addressed with natural fibre matting T-Juta 500 and the synthetic geomat T-Mat.
- Drainage. This is where T-Mix Drain 20 SS comes in, the cuspated-fibre geomat sandwiched between 2 geotextiles.
- Mechanical protection of waterproofing. The geotextiles from the Tematex NW PET range, in white and black, fit the bill.
- Published in BUILDING, Flat green roofs
Technical considerations in building reinforced soil walls
Reinforced soil walls have proved highly popular in recent years and are produced wherever possible, taking the place of concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems.
Employed in a range of different environments, they bring significant advantages, both financial and environmental. Indeed, unlike concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems, they:
- are sustainable because they give a vegetated finish;
- are a great space-saving solution, with slopes as steep as 80° (compared to the 30-40° of natural soil embankments);
- result in less pollution given the smaller number of trucks required to carry construction materials;
- make use of the excavated earth for backfilling, provided it is compatible with stability standards, meaning no more material needs to be brought in;
- blend seamlessly with their surroundings once the slopes are grassed over, without becoming a blot on the landscape of our villages.
Whatever the case, before planning the work, there are a number of aspects and data to be taken into consideration.
Preliminary data needed
To start with, all essential technical information must be procured in order to be able to assess the feasibility of the project, such as:
- geological testing of the area on which the wall is planned to be built
- topographical surveys
- meaningful cross-sectional drawings showing the current condition
- geometry of the planned wall (face angle, height, division into tiers, slope on top)
- external loads applied to the structure (top loads in the event it needs to accommodate a car park or a road)
- what earthquake risk zone the area is in
- geotechnical properties (angle of shearing resistance, cohesion and density) of the earth behind the future wall, of the foundation soil, and of the backfill
- whether there are perched aquifers or seepage of a different nature.
At this point, the next step is to check design calculations using specific software.
Checking design calculations
Checking is performed to assess both internal and external stability. The following tests are carried out in the former case:
- reinforcement strength test, which assesses possible failure mechanisms and determines the spacing, length and tensile strength of the geosynthetics due to be laid
- pull-out test to check that the reinforcement applied does not break or slide out
- direct sliding test, to ensure there is no translational movement across the installation planes
- wrap-around test, to ensure that the length wrapped around the top of each individual layer is stable.
The checks to be carried out during the project’s execution to assess external stability consist in sliding, overturning, bearing capacity and global failure analysis.
Do you want to chat with one of our experts to find the solution that best suits your requirements?
We have 30 years of experience in the industry and can give you access to materials and solutions offering specific performance. Contact us!
Do you want to learn more about the full TeMa Geo Solutions product range for reinforced earth structures? Click here.
Cycle and pedestrian paths: solutions to make them safer and more attractive.
Longer days, milder afternoons, a great desire to spend time outdoors and perhaps get some physical exercise, but also go to work and school or visit a friend… These are all good reasons for using, when available, cycle and pedestrian paths, possibly far from urban traffic.
The advantages of sustainable mobility
We are increasingly talking about environmental sustainability and the physical and psychological benefits of physical exercise:
- Less air and noise pollution caused by traffic.
- Reduced transport costs.
- Greater freedom of movement.
- Enhanced green areas in cities.
- Better quality of life by doing a bit of sport on a daily basis.
TeMa Geo Solutions for safety and urban benefits
‘Unequipped’ roads can be hazardous for those who choose to get around by bicycle: for this and environmental reasons, cycle and pedestrian paths are the ideal solution, as they are increasingly becoming part of local government mobility plans.
TeMa Geo Solutions offers all its experience by combining reinforced earth structures and their feature of being green, with cycle and pedestrian paths.
An embankment can be made or a road widened with its sides sloping at 65°/70° using the T-System (consisting of formworks, X-Grid PET geogrids and K-Mat FG Green erosion control mats as facing), thereby making the path safe and allowing a slope to turn green again. Making a slope green again provides a natural erosion control function: to encourage it, TeMa Geo Solutions recommends installing natural or synthetic mats. To make the structure stable, the T-System for reinforced soils adopted by TeMa involves using X-Grid PET geogrids.
Controlling surface erosion with biomats and geomats
Soil erosion is an almost inevitable natural phenomenon that has become a greater concern in recent years due to the worsening climate situation – in Italy, for example, 132 extreme weather events were recorded between January and July 2022, a higher number than the annual average over the last decade – combined with long periods of drought.
Strong winds, heavy rain, hail and runoff tend to remove the surface layer of exposed soils, which often include organic matter and seeds. Climate change facilitates erosion, making it not only inevitable but also hazardous if left uncontrolled.
It’s essential to counter or mitigate the phenomenon: soil provides us with food, biomass and raw materials; human activities take place on it and it’s part of the landscape and our cultural heritage.
Which structures are more subject to surface erosion?
The areas of application most affected by the erosive action of the climate are:
- slopes and the sides of landfills and contaminated sites, and those that have been grassed for appreciable aesthetic improvement;
- reinforced earth structures, more specifically terracing in vineyards and the embankments of canals or rivers;
- ascending/descending ramps from flyovers, tunnel entrances and noise barriers on roads and railways;
- dry, rocky slopes, of all angles, that shape the terrain of Italy.
The effects of surface erosion
The uncontrolled removal of the surface topsoil and the failure of vegetation to take root results in ‘thinning’ of the soil and a risk to the stability of sloping areas.
What can be done to prevent surface erosion?
We should begin by pointing out that a case-by-case assessment is required that considers many variables, such as the nature and uniformity of the soil, the slope gradient, the type of slope (dry or rocky) and the weather conditions in the area where intervention work is to be carried out.
In general, vegetation, whatever type it is, has a natural ability to protect soils from erosion. So the best course of action is to quickly encourage grassing and then apply biodegradable mats made of jute, straw, coconut and cellulose fibre, which can also be pre-seeded.
TeMa Geo Solutions recommends biomats such as Ecovermat, Ecovermat P and PC, and Ecovernet.
Alternatively, or combined with these, synthetic geomats, mainly made of polymer monofilaments, can be used.
Once laid, they are covered with another layer of soil: in this way, the roots of growing vegetation will become entangled with the geomat, creating an almost permanent erosion protection system.
Once again, TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide range of geomats to choose from.

Uncertain about what to choose? We can help you. CONTACT US!
TeMa even more transparent about sustainability
With the new EPD certification, TeMa Technologies and Materials provides information about the level of sustainability of its products: this includes most of the membranes and geocomposites manufactured on its production lines. For 30 years, TeMa has regarded environmental protection as a duty and obligation towards the community and future generations.
What is EPD and what is analysed to obtain it?
The Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) is a document that provides specific data on the life cycle of products or a service. It measures the impacts that the production and life phases of a product have on the environment by means of a Life Cycle Assessment to determine the consumption of resources such as water, materials and energy.
It is voluntary and verified by the independent third party SGS so that certified declarations can be given to clients.
International acknowledgement
The EPD document is internationally acknowledged, as it complies with ISO standards. This ensures use, credibility and stability over time, making the data collected available for use in any type of environmental management system and providing information for environmental certification protocols for buildings and infrastructures.
Which product lines from TeMa Building Solutions are EPD certified?
The products having obtained EPD certification are:
- the studded membrane line, which includes Membrana Nera, Membrana Nera Geo, T-Kone, Tefond, HDD, TM and MD;
- the monofilament drainage line comprising Q-Drain C and Q-Drain ZW;
- the anti-erosion and reinforcement geomat line, which includes K-Mat and X-Grid AM.

Our certificates can always be consulted by clicking here and entering TeMa in the filters.
- Published in CORPORATION, news, TeMa Technologies and Materials
Reinforced earth structures as noise barriers
Hearing the noise of traffic outside your window all day long is irritating and distracting and, in the long term, also harmful to your health.
This is why the WHO and a number of laws govern the use of noise remediation systems in cities: the Framework Law no. 447 of 1995 for Italy and the European Directive on Environmental Noise no. 49/2022. If the cause of the noise cannot be addressed, the solution is to install protective barriers. Various kinds can be used, but in this case we focus on reinforced earth structures that require specific measures, which we discuss here.
For example, the Pedemontana Veneta is a new toll motorway in Italy: nearly 100 km long. Almost entirely in operation in the north-east of the Veneto region, the main route of this motorway runs through a deep trench in order to minimise the ‘territorial’ and environmental impact on the surrounding area. This means that long sloping areas of reinforced earth can be found along the sides of the motorway, with rows of trees and hedges for 58.61 km and green areas covering 1,333,410 square metres of hedgerows, groves, grassy slopes and tree-lined meadows.
A focus on noise with much regard for the landscape.
What do reinforced earth noise barriers consist of?
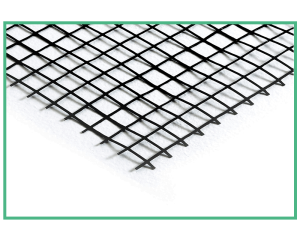
For this type of embankment with its typical trapezoidal shape, earth is used that will be covered by vegetation over time. Geosynthetic reinforcements and geogrids are added to support the earth, which already has good compressive strength. These are inserted horizontally into the ground and develop friction and tension that stabilise the structure, increasing its resistance to stress.
The TeMa Geo Solutions offer includes the X-Grid Pet PVC range of geogrids, with different resistance values, which are ideal for all kinds of contexts.
Another aspect to bear in mind is surface erosion of the soil: to counteract this, synthetic geomats are applied, also with a mulching function to encourage the growth of grass cover, or natural fibre bionets.
Also in this case, TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide choice ranging from Ecovermat F Grass and Ecovernet FJ to the K-Mat range.
Why use a vegetation barrier as a protective noise barrier?
A vegetation barrier has an unquestionable ability to limit the spread of sound waves: some of them are absorbed, some reflected and some deflected. As a result, the amount of sound waves reaching the receiver is greatly reduced and noise can be dampened by several decibels.
The advantages of a reinforced earth sound-deadening barriera
Creating reinforced earth structures brings considerable advantages:
- it costs less because you can often use earth available on-site
- no special maintenance is required other than regular trimming.
- it helps the environment and integrates with it: the use of vegetation also reduces vehicle emissions by absorbing CO 2 and purifying the air.
- 1
- 2











